A telephone remote control system is designed. The system uses AT89C2051 single-chip microcomputer and MT8870 dual-tone multi-frequency decoding integrated circuit as the core. With the help of public telephone network, intelligent control of remote devices is realized by telephone. The article introduces the composition, working principle and programming method of the system. The ringing detection and analog hooking control circuit are described in detail. Users can use any of the dual-tone multi-frequency phones (including mobile phones and telephone extensions) outdoors, and can remotely control various electrical appliances (such as rice cookers, microwave ovens, etc.) according to voice prompts. This device is suitable for homes, enterprises, institutions, shops and other places. It is easy to operate and reliable in system performance. It is a technological product with promising prospects in the future.
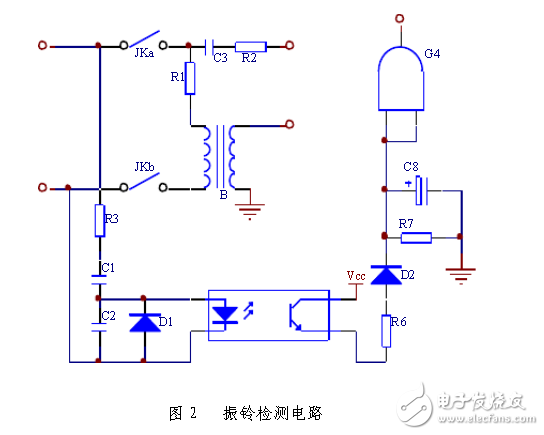
Ring detection circuit
Circuit working principle : The ringing detection circuit is composed of components such as an optocoupler LE and a gate circuit G4. When the telephone line has no ringing current, the line voltage provided by the telephone exchange is a DC signal of 48V-60V. When the user calls, the telephone switch sends a ringing signal, and the 89C2051 single-chip microcomputer drives the circuit control device such as the switch control circuit, the DTMF signal decoding circuit, the ringing current detection circuit and the voice prompt circuit. At this time, the light-emitting diode of the optocoupler LE is turned on, so that the phototransistor is turned on, so the +5V power supply charges the 100uF capacitor through the 1K resistor and the diode. When the voltage on the capacitor is charged to the open level, the AND gate G4 outputs a high level and is detected by P3.5 of the AT89C2051. Each time the ring is ringed, the gate G1 outputs a high level, that is, a positive pulse. The ringing signal is a sine wave of 25±3V, the effective value of the voltage is 90±15V, and the ringing is in the period of 5s, that is, 1s is sent for 4s. The positive pulse signal can be directly output to the interrupt counter input port of the single-chip microcomputer to complete the process of detecting and counting the entire ringing tone. The circuit diagram design is based on the characteristics of the ringing signal, and the ringing detection circuit is designed as shown.
Pick up control circuit
Circuit working principle: AT89C2051 first detects the output of gate G4 from P3.5, G4 outputs a positive pulse every time, the telephone rings once; P3.5 must detect 8 positive pulse signals before sending low power from P1.1 The transistor T7 is turned on, so the relay JK pulls the two pairs of normally open contacts JKa and JKb closed, and the 500 ohm resistor <in series with the small audio transformer winding> is connected to the telephone line, realizing the analog lift. Then P3.2 waits for the positive pulse of the STD terminal of the DTMF decoder. Once the positive pulse of the STD terminal is recognized, P3.0-P3.4 reads the binary code information of the output of the DTMF decoder. This information is the remote command, AT89C2051 can It is used to determine whether it is a password or a command to open or close a certain route or an on-hook command.
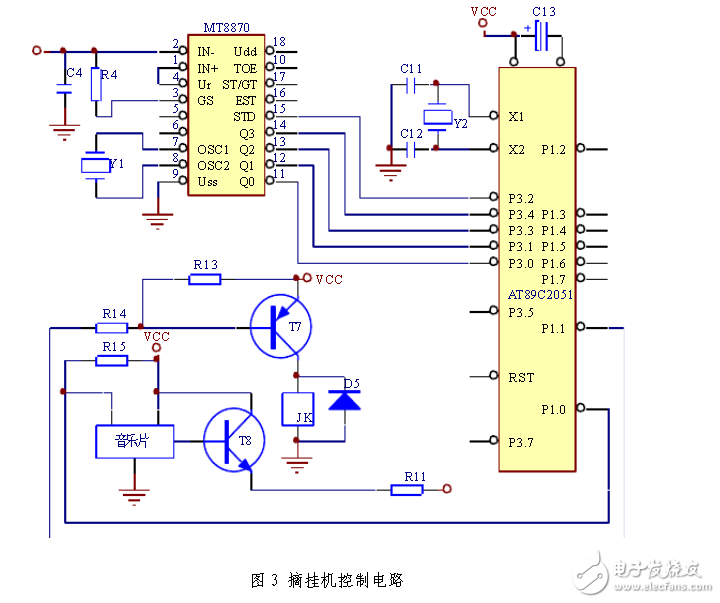
The execution signal of the on-hook command is output from P1.1. When P1.1=1, T7 is cut off and the relay is released, that is, the analog on-hook is realized. The signal for controlling the action of the controlled object is outputted from P1.3-P1.7 for a total of 5 channels. For example, if P1.3=1 enables T1 to be turned on, relay J1 pulls in; if P1.3=0, then J1 freed. If P1.7=1, T5 can be turned on, relay J5 can be closed; if P1.7=0, then J5 is released. However, as can be seen from the figure, P1.3 is not directly connected to T1. P1.7 is not directly connected to T5, but is separated by an integrated block 74LS273. 74LS273 is an 8D latch, that is, the chip contains 8 D flip-flops, the input is D0-D7, and the output is Q0- Q7. If the clear terminal CLR is low, the device is reset to zero, and the Q0-Q7 outputs are all zero. If the clear terminal is high, whenever the trigger terminal CLK has a level transition, the input terminal The state of D0-D7 is latched into the device and output from Q0-Q7. This state is remembered forever as long as the CLK terminal is no longer triggered. It can be seen that the signal output from the AT89C2051 from P1.3-P1.7 is only sent by the 74LS273 and then sent out. The control logic is the same as the T1-T5 directly connected. The necessary condition for the input terminal D0-D7 of the 74LS273 to accept the input signal is that there is a positive transition on the CLK terminal. This must satisfy two conditions at the same time: First, the STD end of the DTMF decoder must be high, that is, remotely transmitted. The terminal has DTMF signaling to send; the second is that the P1.2 of the AT89C2051 must send a hopping signal that changes from ‚0 to 1. Only when the two conditions are satisfied at the same time, the gate G5 outputs the positive transition signal, and the 74LS273 can accept the external information, which greatly improves the anti-interference ability of the circuit and prevents the controlled object of the AT89C2051 from being accidentally interfered. Malfunction.
ShenZhen Antenk Electronics Co,Ltd , https://www.antenkconn.com