Relays are commonly used components in electronic circuits. In general, electronic switch drive circuits composed of transistors, relays, etc., often add additional circuits to change the operating characteristics or protection of the relay. The additional circuit of the relay mainly has the following three forms:
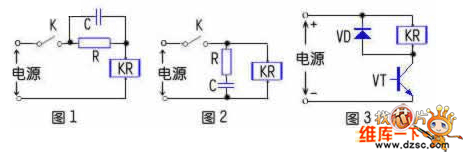
1. Relay contact protection circuit _ relay series RC circuit diagram: The circuit form is shown in Figure 1. This form is mainly used in circuits where the rated operating voltage of the relay is lower than the power supply voltage. When the circuit is closed, the self-inductance of the relay coil will cause the electromotive force to hinder the increase of the current in the coil, thereby prolonging the pull-in time. After the RC circuit is connected in series, the pull-in time can be shortened. The principle is that at the moment when the circuit is closed, the voltage at the voltage across the capacitor C cannot be abruptly changed as a short circuit, so that a power supply voltage higher than the rated working voltage of the relay coil is applied to the coil, thereby accelerating the speed of the current increase in the coil, so that the relay Quickly pull in. After the power supply is stable, the capacitor C does not work, and the resistor R acts as a current limiting.
2. Relay contact protection circuit _ relay parallel RC circuit diagram: The circuit form is shown in Figure 2. After the circuit is closed, the RC circuit does not work when the current is stable. When the circuit is disconnected, the relay coil self-inductively generates an induced electromotive force through the RC circuit. The discharge causes the current decay in the coil to slow down, thereby prolonging the release time of the relay armature and acting as a delay.
3. Relay contact protection circuit _ relay parallel diode circuit diagram: circuit form shown in Figure 3, mainly to protect the drive components such as transistors. When the transistor VT in the figure is turned from off to off, the current flowing through the relay coil will rapidly decrease. At this time, the coil will generate a high self-inductance. The electromotive force is superimposed on the power supply voltage and added between the c and e poles of the VT. The transistor will be broken down. After the diode is connected in parallel, the self-induced electromotive force of the coil can be clamped to the forward voltage of the diode. The value of the silicon tube is about 0.7V, and the tube is about 0.2V, so as to avoid breakdown of the driver such as a transistor. Device. When paralleling the diode, pay attention to the polarity of the diode can not be reversed, otherwise the drive components such as transistors are damaged.
Yuhai company develop and produce of various rings sizes, bearing variety of electrode and metallisation configurations. This variety of Rings is fabricated from various material formulations for applications such as high power, sensitivity, stability.
Features
· • electrode type on request
· • Surface roughness on request, for specific demanding application
· • Thickness/Radial frequency tuning available on request
• Wide choice of PZT formulations
Applications include
• Sensors
• Welding
• Ultrasonic cleaning
• Precise Measurement
• Ultrasonic scalpel
• Cauterisation
• Phacoemulsification
• Therapeutic ultrasound
• Accelerometers
Dimension range
|
Outer diameter |
3-180mm |
|
Inner diameter |
1-150mm |
|
Thickness |
0.2-25mm |
Piezo Ring,Pzt Ring,Piezoelectric Ceramic Ring,Piezo Ceramic Ring
Zibo Yuhai Electronic Ceramic Co., Ltd. , https://www.yhpiezo.com