Circuit function and advantage
The circuit shown in Figure 1 is a flexible signal conditioning circuit that handles signals with a wide dynamic range (from a few mV pp to 20 V pp). The circuit utilizes a high-resolution analog-to-digital converter (ADC) internal programmable gain amplifier (PGA) to provide the necessary conditioning and level shifting and dynamic range.
±10 V full-scale signals are very common in process control and industrial automation applications; however, in some cases, the signal may be as small as a few mV. Attenuation and level shifting must be performed when processing a ±10 V signal with a modern low voltage ADC. However, for small signals, amplification is required to take advantage of the dynamic range of the ADC. Therefore, when the range of variation of the input signal is large, it is necessary to use a circuit with a programmable gain function.
In addition, small signals may have large common mode voltage swings; therefore, high common mode rejection (CMR) performance is required. In some applications where the source impedance is large, the analog front-end input circuit also needs to have high impedance.
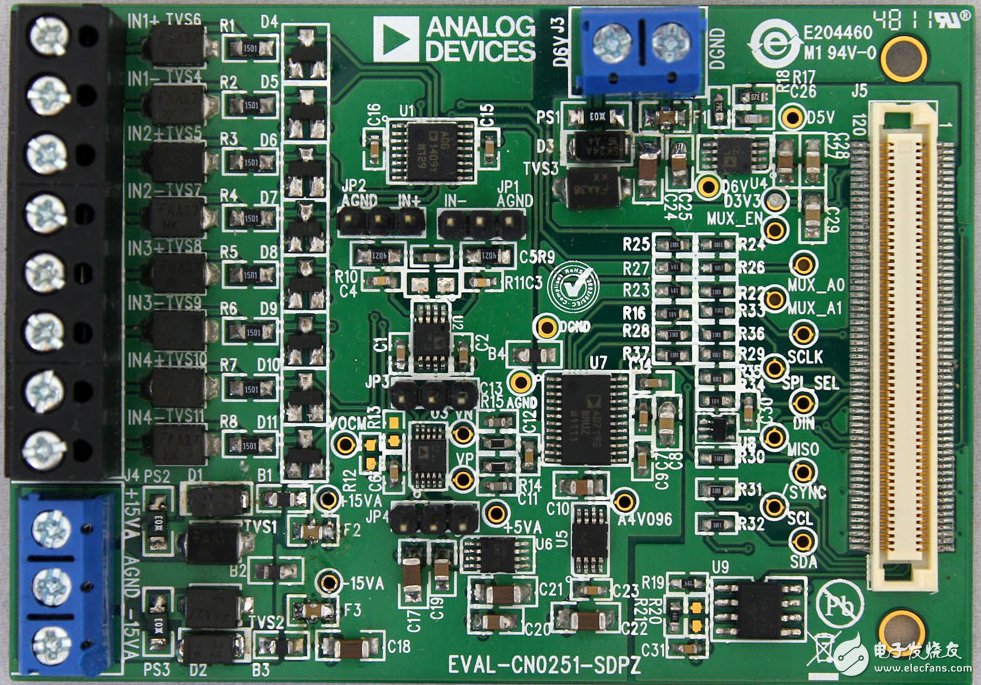
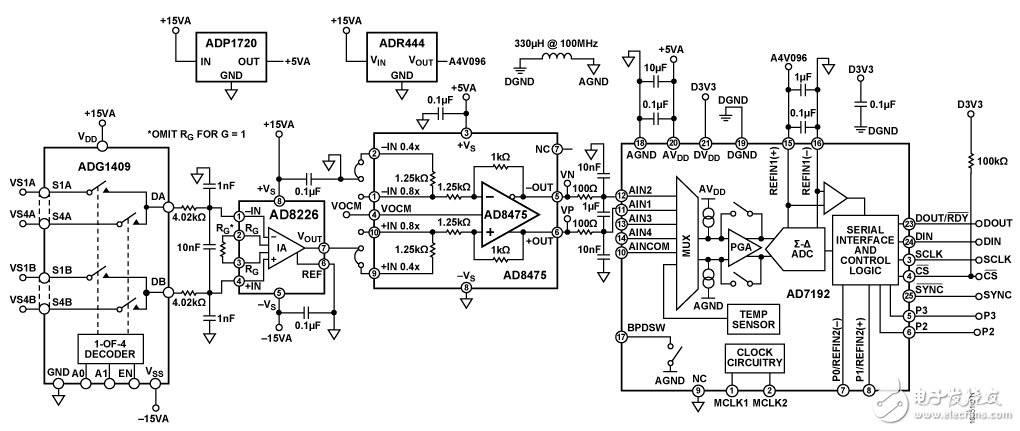
Figure 1. Flexible analog front-end circuit for wide industrial range signal conditioning
The circuit shown in Figure 1 solves all of these challenges and provides programmable gain, high CMR, and high input impedance. The input signal goes through the 4-channel ADG1409 multiplexer into the AD8226 low-cost, wide input range instrumentation amplifier. AD8226 Low Cost, Wide Input Range Instrumentation Amplifier. The AD8226 offers high common mode rejection (CMR) of up to 80dB and very high input impedance (differential mode 800ΩM and common mode 400ΩM). The wide input range and rail-to-rail output allow the AD8226 to take full advantage of the supply rail.
The AD8475 is a fully differential attenuating amplifier with integrated precision gain resistors that provide precision attenuation (G=0.4 or G=0.8), common-mode level shifting, and single-ended differential conversion. The AD8475 is an easy-to-use, fully integrated precision gain block that can handle signal levels up to ±10 V from a single supply. Therefore, the AD8475 is suitable for attenuating signals from the AD8226 up to 20Vp-p while maintaining high CMR performance and providing a differential output to drive the differential input ADC.
The AD7192 is a 24-bit Σ-Δ ADC with a built-in PGA. An on-chip low noise gain stage (G = 1, 8, 16, 32, 64, or 128) means that small signals can be input directly to the ADC.
In combination with the above devices, the circuit provides very good performance and is easy to configure for signals that vary in amplitude. This circuit is suitable for industrial automation, process control, instrumentation and medical device applications.
Feed Through Terminal Block Section
Feed Through Terminal Block.
In the electrotechnics, the terminal refers to the terminal and is designed to run through the terminal production. The type is divided into single hole, double hole, socket, hook, etc. from the material, copper silver plating, copper zinc plating, copper, aluminum, iron, etc. their functions are mainly to transmit electrical signals or conduct electricity. The unit of terminal block is "bit", and one wiring bit is "bit". Usually the so-called table is the serial number of the terminal, which has different definitions in different applications. "Jie" and "bit" have the same meaning, but they are called differently. Groups are made up of sections.
Feed Through Terminal Block
ShenZhen Antenk Electronics Co,Ltd , https://www.atkconnectors.com