In the circuit, when the power is further increased or multiphase rectification is required for other reasons, a three-phase rectifier circuit is proposed. Figure 1 shows the schematic diagram of a three-phase half-wave rectification circuit. In this circuit, each phase of the three phases separately forms a half-wave rectification circuit, and the three voltage half-waves that are rectified are superposed by 120 degrees in time, and the rectified output waveform is only 0 points, and in one cycle. There are three rectified half-waves with a width of 120 degrees. Therefore, the capacity of its filter capacitor can be smaller than that of single-phase half-wave rectification and single-phase full-wave rectification.
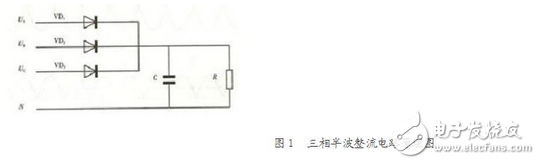
The wiring diagram of the resistive load three-phase half-wave controlled rectifier circuit connected to the resistive load is shown in Figure 3-10a). The primary winding of the rectifier transformer is generally connected in a triangle, so that the third harmonic current can flow, so as to ensure that the transformer potential does not be distorted, thereby reducing harmonics. The secondary winding is a star connection with a neutral line.
1. Resistive loadThe wiring diagram of the three-phase half-wave controllable rectifier circuit connected to the resistive load is shown in Figure 3? XML: NAMESPACE PREFIX = ST1 / "-10a). The primary winding of the rectifier transformer is generally connected in a triangle, so that the third harmonic current can flow, so as to ensure that the transformer potential does not be distorted, thereby reducing harmonics. The secondary winding is a star connection with a neutral line, the three thyristor anodes are respectively connected to the three-phase of the star, and the cathodes are connected together to the midpoint of the star. The connection of the thyristor cathodes together is called a common cathode connection. The common cathode connection method is convenient for arranging a trigger circuit with a common line, and is widely used.
The operating characteristics, waveforms and basic quantities of the three-phase controlled rectifier circuit are not only related to the load nature, but also have a great relationship with the control angle α. They should be analyzed according to different α.
(1) α=0oIn the three-phase controlled rectifier circuit, the calculation starting point of the control angle α is no longer selected at the zero crossing point where the phase voltage is positively changed from negative to negative, and is selected at the intersection of the phase voltages, that is, the natural commutation point, as shown in Fig. 1b) 1, 2, 3, 1, ... and so on. Thus, α=0 means that a trigger pulse ug1 is applied to the gate of the thyristor VT1 at ωt1; a trigger pulse ug2 is applied to the gate of the b-phase thyristor VT2 at ωt2; and a gate of the thyristor VT3 is applied to the gate of the thyristor VT3 at ωt3 The trigger pulse ug3 is applied, etc., as shown in Figure 1c).
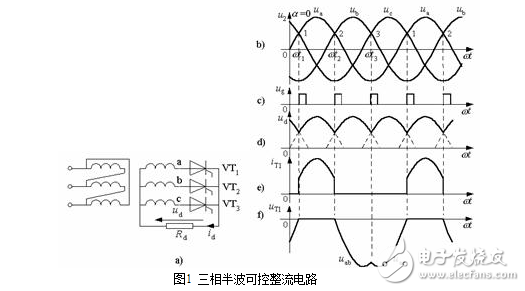
In the common cathode connection three-phase half-wave rectification circuit, the conduction principle of the thyristor is which phase voltage is the highest and the components connected to the phase will be turned on. If it is assumed that the circuit operation has entered a steady state, the c-phase VT3 is conducting before the time ωt1, then the a-phase voltage ua is the highest during the period ωt1 to ωt2, and the VT1 has the conduction condition. At the time of ωt1, the trigger pulse ug1 is applied to the gate of VT1, VT1 is turned on, and the voltage of phase a is obtained on the load Rd, that is, ud=ua, as shown in Fig. 1d). During the period of ωt2~ωt3, the ub voltage is the highest, the trigger pulse ug2 is applied to the VT2 gate at ωt2, VT2 is turned on, and the b-phase voltage is obtained on Rd, ud=ub. At the same time, the potential at point b is applied to the anode of VT1 through the turned-on VT2. Since ub>ua at this time, VT1 is turned off by the reverse anode voltage. VT2 is turned on and VT1 is turned off, thus completing a commutation. Similarly, the commutation process from VT2 to VT3 will occur again at time ωt3. It can be seen that for a three-phase controlled rectifier circuit with a common cathode connection, the commutation is always switched from a low potential phase to a high potential phase. In order to ensure normal commutation, the phase sequence of the trigger pulse must be consistent with the power phase sequence. Since the three-phase power system is balanced, the three thyristors will continue to circulate in the same manner, and each tube is turned on for 1/3 cycle.
The common-cathode connection three-phase half-wave rectification circuit outputs a DC voltage waveform as a positive half-cycle envelope of a three-phase AC phase voltage, which is a pulsating DC, pulsing three times (three waves) in one cycle, and the lowest pulsation frequency is Three times the frequency. For resistive loads, the load current id waveform is the same as the load voltage ud waveform. The transformer secondary winding current i2 is the current iT in the thyristor. Therefore, the current waveform in the a-phase winding, that is, the current waveform iT1 in VT1 is the DC ripple current, as shown in Fig. 1d). Therefore, the three-phase half-wave rectification circuit has a DC magnetization problem of the transformer core. The voltage that the thyristor is subjected to is divided into three parts, each of which accounts for 1/3 cycle. Taking the voltage uT1 on the VT1 tube as an example (Fig. 1f)): When VT1 is on, it is the tube voltage drop, uT1=UT ≈ 0; when VT2 is on, uT1=uab; when VT3 is on, uT1=uac. Under continuous current conditions, no matter how the control angle α changes, the voltage waveform on the thyristor always consists of these three parts, except that under different α, the specific shape of each part of the waveform is different. In the case of α=0°, all the reverse anodic voltages on the thyristors are taken, and the maximum value is the line voltage amplitude.
(2) α≤30°Fig. 2 shows a waveform diagram when α = 30°. Assume that the circuit has entered a stable working state before analysis, and is turned on by the thyristor VT3. When passing through the a-phase natural commutation point, although ua>uc, the thyristor VT1 gate trigger pulse ug1 has not been applied, the VT1 tube cannot be turned on, the VT3 tube continues to operate, and the load voltage ud=uc. At the time of ωt1, exactly α=30°, the VT1 trigger pulse comes, the tube is triggered to conduct, VT3 is turned off by the reverse anode voltage uca, and the commutation of the thyristor VT3 to VT1 or the commutation of the c-phase to the a-phase is completed. Load voltage ud=ua. Due to the three-phase symmetry, VT1 will always conduct to the time ωt2 after 120°, and the commutation of VT1 to VT2 or the commutation of phase a to phase b occurs. The later process is the turn-on conduction of the three-phase thyristor, and the output DC voltage ud is an envelope of the three-phase voltage in the range of 120°. The waveform of the load current id is similar to ud, as shown in Figure 2c). It can be seen that when α=30°, the load current begins to appear zero crossing point, and the current is in a critical continuous state.
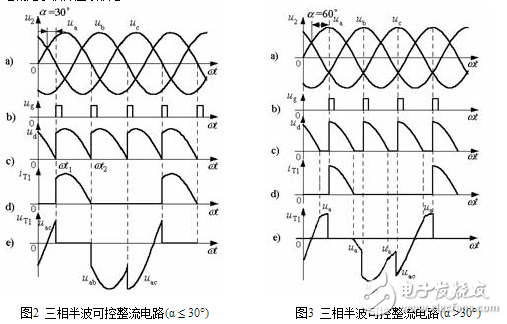
The thyristor current is still DC ripple current, and the conduction time per tube is 1/3 cycle (120°). The thyristor voltage is still composed of three parts, each part occupies 1/3 cycle, but since α=30°, except for the reverse anode voltage waveform and α=0°, the thyristor begins to be positively blocked. The voltage is shown in Figure 2e).
(3) α>30°When the control angle α>30°, the direct current becomes discontinuous. Figure 3 shows the voltage and current waveforms for each of α = 60°. When a phase voltage becomes negative through zero, the phase thyristor is naturally turned off. At this time, although the voltage of the next phase is the highest, the gate trigger pulse of the phase thyristor has not arrived yet, and the thyristor of each phase is not turned on, so that the output DC voltage and current are zero and the current is intermittent. Always go to α=60°, the next phase tube can be turned on. At this time, the conduction angle of the tube is less than 120°.
As the angle α increases, the conduction angle also decreases, and the DC average voltage Ud also decreases. When α = 150°, θ = 0°, Ud = 0. Its phase shift range is 150°. Because the current is not continuous, the voltage on the thyristor is greatly different from the continuous time. Its waveform is shown in Figure 3e).
The DC average voltage Ud should be treated separately in the cases of α≤30° and α>30°.
When α≤30°, the load current is continuous, and the calculation of Ud is as follows
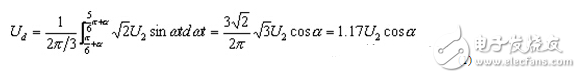
When α=0, Ud=Ud0=1.17U2, the maximum.
When α>30°, the DC current is not continuous.
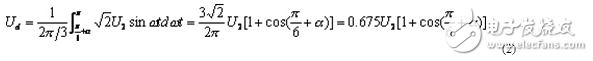
The maximum reverse voltage URM of the thyristor is the line voltage peak  The maximum positive voltage UTM of the thyristor is the voltage difference between the anode and the cathode when the thyristor is not conducting, that is, the peak voltage of the phase
The maximum positive voltage UTM of the thyristor is the voltage difference between the anode and the cathode when the thyristor is not conducting, that is, the peak voltage of the phase  .
.
The three-phase half-wave controlled rectifier circuit under inductive load is shown in Figure 4a). Assuming that the load inductance is large enough, the DC current id is continuous, straight, and the amplitude is Id. When α ≤ 30 °, the DC voltage waveform is the same as that of the resistive load. When α>30° (for example, α=60°, as shown in Fig. 4b), the thyristor does not turn off when the AC voltage crosses zero due to the induced potential eL in the load inductance Ld. Taking the phase a as an example, VT1 is turned on at time ωt1 of α=60°, and the direct current voltage ud=ua. When ua=0 is at ω2, the decrease in ua will cause the current id flowing through Ld to decrease. The polarity of self-induced potential eL will prevent the decrease of id, so that VT1 still bears forward anode voltage. through. Even when u2 is negative, the sum of the self-inductive potential and the negative phase voltage (ua+eL) can still be positive, so that VT1 continues to withstand the forward anode voltage and maintains conduction until VT2 triggers conduction at ωt3, and VT1 to VT2 occur. Switching to the flow. Thus, when α>30°, a negative voltage region appears in the ud waveform, and the thyristors of each phase are turned on by 120°, thereby ensuring continuous load current, so that under large inductive load, although the ud waveform is large, even negative. Value, but the id waveform is straight and the pulsation is small.
Since the current is continuous and stable, the thyristor current is 120° wide and the height is Id rectangular wave, and the current iT1 waveform in the thyristor VT1 is given in Fig. 4b). A region in the range of ωt2 to ωt3 is maintained by the self-induced potential eL of Ld. The voltage waveform on the thyristor is still composed of three segments, each segment occupying 1/3 cycle, as shown in the voltage VT1 on the VT1 tube in Figure 4b). When VT1 is turned on, it does not withstand voltage, uT1=0; when VT1 is turned off, since any other phase thyristor is turned on at any moment, the phase voltage is induced, so that VT1 is subjected to the corresponding line voltage.
The DC average voltage Ud is
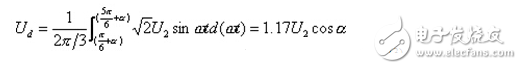
When α=0°, Ud=Ud0=1.17U2 is the maximum; when α=90°, Ud=0, which is reflected in the ud waveform, the areas of the positive and negative voltage regions are equal, and the average value is zero. It can be seen that the phase shift range of the three-phase half-wave circuit is 90° under large inductive load.
Since the thyristor current is a rectangular wave with a width of 120° and a height of Id, the average value is

Thyristor current effective value

The secondary current of the transformer is the thyristor current, so the transformer
Data center energy meter is a measurement device designed specifically for data center server power management.The single phase energy monitoring design exquisite, can for A + B two into line and 96 road for electrical parameters, the input and output parameters of the switch state and the lightning protection device such as real-time monitoring, all alarm threshold measurement channels can be set in A separate, to qualify the limit event trigger system sound and light alarm, immediately on the volume in the traditional instrument, the height of the monitoring circuit integration.

Panel Ac Energy Monitoring Device,Multifunction Three Phase Energy Meter,Single Phase Power Monitoring Device,Wireless Energy Meter For Monitoring System
Jiangsu Acrel Electrical Manufacturing Co., LTD. , https://www.acrel.com.pk