According to the statistics of relevant research institutions, in 2013, the sales volume of mobile phones in the Chinese market was 382.7 million units, of which the sales volume of smart phones reached 32.92 billion units. China has basically completed the replacement process for traditional feature phones. With the advent of smartphones and the new 4G LTE network era, the demand for smart phone batteries will be higher and more stringent. Due to the larger screen size and more complex functions, power consumption will increase. In order to ensure the normal use of mobile phones, it is inevitable to equip high-capacity batteries. Judging from the main mobile phone products in the market, the products around 3000mAH are very common. Regardless of the low-power technology used in the new 4G LTE network, power consumption is a big problem, which also brings the need for a higher capacity battery. According to the feedback from mobile phone R&D engineers, in addition to requiring large-capacity batteries to meet the endurance requirements, the battery also needs to support higher sustained discharge current and instantaneous high current in terms of discharge capacity. The application of these high discharge currents is in conflict with the safety test of the battery itself. Therefore, how to find the balance between them is especially important for battery developers.
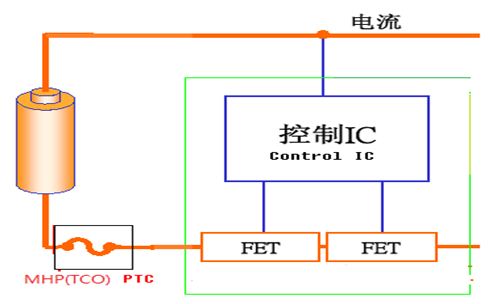
In order to better explain the relationship between the two, we must first understand the lithium-ion battery protection circuit, as shown below, which has a level 1 active protection IC + MOSFET and a 2 level passive protector PPTC or MHP-TA.
UL2054, the most common safety standard in the battery industry, has overcharge test requirements.
The UL2054 short-circuit principle and exception clause for internal components of the battery stipulates that if it is a non-certified protection device, it will be short-circuited during the test.
The principle of Fault is as follows:
a. The device with safety certification is not fault;
b. Any non-certified protection component will be Fault (short circuit), usually like Mosfet, the current sense resistor will be shorted during the test;
The UL2054 overcharge test method is that the sample cells used for testing are charged at a constant current of 10*C5(2C) (some manufacturers require more stringent requirements of 1C), and each battery or cell is labeled with a thermally coupled component. Then charge until the battery or cell explodes, leaks, or the temperature of the surface of the enclosure returns to ambient temperature or reaches a steady state. In the test, the overcurrent and thermal protection devices must be certified for safety and should be short-circuited without an approved protective device. The UL2054 indicator requires no fire or explosion.
Analysis of the above safety test requirements, it can be determined that in the selection of the secondary passive protector, the lower the protection point of the device, the better the protection effect. In the PPTC device, the smaller the operating current (Itrip) of the device, the easier it is to test; the temperature sensing bimetal device MHP-TA is the lower the operating temperature of the device itself, the easier it is to operate. It's easier to pass the test.
However, in practice, the opposite is true. It is usually required that the battery can meet the short-time maintenance of high-current power supply, and even maintain high current (4A) at high temperature (up to 60 degrees Celsius). This is reflected in the fact that the protection device itself requires the PPTC to have a large holding current (Ihold) at high temperatures. There are certain contradictions in the requirements of these two aspects. One-sided guarantees cannot guarantee product safety and practical application. The selection of passive protection devices MHP-TA and PPTC is closely related to the actual application conditions, structural design, and reference test standards. It is necessary to find a balance between the two. This requires the battery development and design personnel to fully communicate with the protection device supplier in the early stage of development, and at the same time cooperate with sufficient experimental verification to meet the safety requirements of the safety test and meet the practical application. As a leader in the circuit protection industry, TE has many years of experience in the development and application of lithium-ion battery protection devices. Its PPTC and MHP-TA have been widely used in mobile phone battery manufacturers at home and abroad.
Used in small offices, home offices, mobile users, online games, and other environments
Dongguan Bofan technology Co., LTD , https://www.pengliandz.com