According to foreign media Electronicsweekly, Microchip Technology Inc. announced that it will double the throughput of its low-pin-count 32-bit PIC microcontroller (MCU) series, according to foreign media Electronicsweekly. At the same time, the memory capacity will be expanded by 3 times, and the MIPS32 M4K processor will be updated and applied to the company's latest PIC32MX series processor.
In addition, Microchip has added peripherals and released a development tool that introduces third-party firmware for the company's integrated development environment (IDE), which can be purchased at microchipDIRECT.
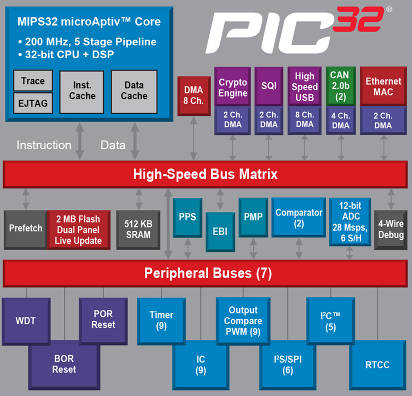
PIC32MX is a high-performance general-purpose series and USB series 32-bit flash microcontroller. The main features are:
? High performance 32-bit RISC CPU
? MIPS32? M4K? 32-bit core with 5-stage pipeline
? Frequency up to 80 MHz
• Zero wait state flash access performance of 1.56 DMIPS/MHz (Dhrystone 2.1)
Single-cycle multiplication unit and high-performance division unit
• MIPS16e? mode allows code compression up to 40%
• 32 32-bit kernel file registers for each group to reduce interrupt latency
• Prefetch cache module speeds up execution from flash
(Component trading network Longyan compiled)
Foreign media original:
Microchip doubled the throughput and quadrupled the memory of its 32bit PIC family, and released a tool which brings third-party firmware into the firm's integrated development environment (IDE), as well as adding new peripherals.
Most of the up-grade has come from replacing the original MIPS M4K CPU, as used in the most recently announced PIC32MX family, with a MIPS microAptiv core, creating what will be known as thePIC32MZ family.
Performance is 330Dmips (at 200MHz) and 3.28CoreMarks/MHz – the former giving 1.65Dmips/MHz, which is the same Dmips/MHz and CoreMarks/MHz as the M4K.
The difference is that the older MX family did not have cache and could only only run at 100MHz, while Microchip has selected the with-cache flavour of microAptive.
"We have chosen the cache option, and a pretty large size cache. You can lose some predictability, but the overall performance is greatly improved. It's definitely worth it," company product marketing manager Bill Hutchings told Electronics Weekly.
"The M4K and the microAptiv core offer the same performance efficiency in 32bit mode of operation, termed MIPS32 mode, so that is why the Dmips/MHz numbers are the same. The microAptiv core offers additional capability such as the cache which enables the higher clocking Frequency by providing instructions and data that can be accessed at full rate."
As well as running in MIPS32 mode for legacy code, the microAptive core can also execute the 16/32bit microMIPS instruction set – originally introduced by MIPS to improve code density in the MK14, a later core than the MK4.
The older MK4 also offered a 16bit mode, called MIPS16e ASE (application specific extension).
"MicroAptiv offers the microMIPS instruction set which has a code density similar to MIPS16, but at near full rate execution: 1.57Dmips/MHz," said Hutchings. "PIC32MX devices [M4K] can have similar code density when operating in MIPS16 mode, but Performance efficiency is impacted."
Producing microMIPS code takes the same effort as producing MIPS32 code.
"Most people will use microMIPS mode. It's completely transparent to the user, just flick a switch in compiler and it will start generating microMIPS," said Hutchings
A flexible printed circuit board is a type of PCB designed to meet the needs of flexible electronic circuits. Originally designed flexible printed circuits to replace traditional wiring harnesses.
Flexible printed circuits are produced using flexible laminates. The flexible laminate holds the conductive foil as well as the dielectric substrate. Flexible circuit boards can be three-dimensionally routed and can be appropriately shaped to fit the available space.
Flexible PCB,Flexible Circuit Board,PCB Production Process,PCB Process Technology,Circuit Board Manufacturing Process
Huizhou Liandajin Electronic Co., Ltd , https://www.ldjpcb.com