Thoughts on the application of cloud computing in telecommunications
Cloud computing is a computing concept developed on the basis of grid (Grid), utility (UTIlity) and software as a service (SaaS) computing. Therefore, it has some conceptual overlap with distributed, grid and utility computing, and at the same time has its own unique meaning when applicable. Today, people associate cloud computing with a higher level of cloud abstraction. Because cloud computing is an emerging computing model, users can use various terminals to access required applications at any place and at any time. These applications are deployed in geographically dispersed data centers. These data centers can dynamically provide and share computing resources. This approach significantly reduces costs and improves economic benefits.
From a technical perspective, the cloud is an infrastructure on which one or more frameworks are built. Figure 1 shows the architecture of the cloud. The virtualized physical hardware layer provides a flexible and adaptive platform that can improve resource utilization and embody the concept of cloud computing in a layered model. From the perspective of layering, cloud computing can be based on IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service), PaaS (Platform as a Service), and SaaS (Software as a Service), so as to implement and realize corresponding business requirements at various levels. 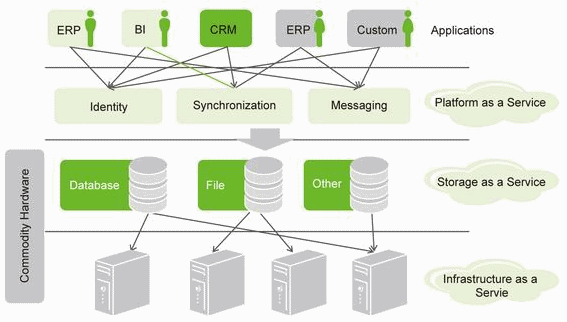
Figure 1 Cloud computing architecture
Cloud computing standardization needs to be improved
For new technologies, there is a suitable time for standardization. As shown in Figure 2, the best opportunity for standardization is in the window period when the technical research has been relatively mature, but the market commercial scale is not large. Standardization earlier than this window period will lead to immature technological development and stifle the potential of technological development. Standardization will be carried out later than this window period. Since a large number of products are already in commercial use, the market cannot afford the cost of standardization, thus forming a de facto set of standards, leading to the failure of standardization. 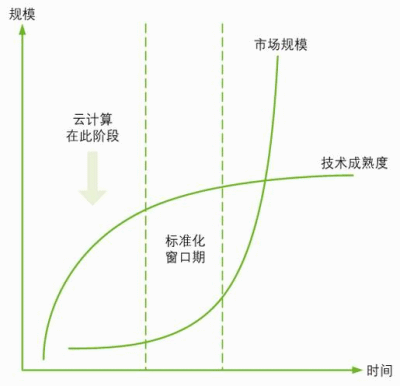
Figure 2 The current standardization stage of cloud computing
On the one hand, current mainstream software and hardware manufacturers, such as IBM, Microsoft, Oracle, SUN, Redhat, Symantec, etc., have all proposed their own cloud computing architectures and systems, and have invested a large amount of R & D power. In each cloud computing architecture, the concepts are vaguely similar, but the details are different. Moreover, due to the different market environments of various manufacturers, there is a big difference in the understanding of cloud concepts and perspectives.
On the other hand, there are still many technical problems to be solved in cloud computing, such as security problems in cloud environment, QoS problems, the problem of virtualizing multiple weak physical machines into a powerful virtual machine, etc. These problems are not in the industry. Commonly approved standardization plan. When real technology is implemented, different cloud computing architectures must adopt one's own private technology for one or more of these problems. Because these technologies are still being explored, it is difficult to standardize in a short time.
When Dr. Ma Weiying, the executive vice president of Microsoft Asia Research Institute visited the IT Longmen array on June 9, 2009, he said frankly: "Now it is the time for various manufacturers to strive forward, and the standard setting environment is not yet mature; After the industry slowly develops to a certain stage, standard setting will come naturally. "
Since cloud computing technology is not yet mature, it can be considered that cloud computing is currently in the early stage of the standardized window period.
The development stage of cloud computing
The "HypeCycle" theory refers to the growth curve of Silicon Valley technology companies and related technologies discovered by Gartner. As shown in Figure 3, a new technology will go through five stages from the initial stage of development to its final commercial success. 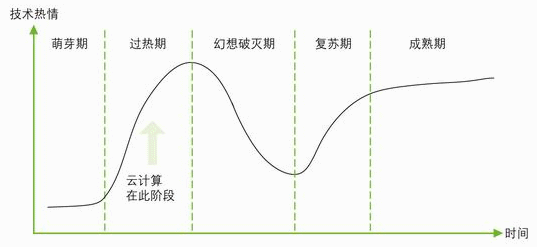
Figure 3 HypeCycle cycle of cloud computing
Jackie Fenn, chief analyst of the "Special Report on the 2009 Hype Cycle" concluded: "Technologies that were in the overheating period during 2009 include cloud computing, e-book readers and Internet TV, while social and microblogging sites have ¬ After the overheating period, it will soon enter a period of disillusionment, and it will gradually be forgotten by corporate users. "
At present, the industry has generated a lot of unrealistic expectations for cloud computing. According to Gartner's analysis and references to historical laws, it is reasonable to believe that cloud computing is currently in the overheating period of the HypeCycle cycle.
Thinking of Cloud Computing in Telecommunication Application
In the cloud computing boom, how should the telecommunications industry respond to ensure that it does not lag behind in future competition?
First, under the premise of imperfect standardization and key technologies to be solved, the initial cloud computing environment will be difficult to fully open. There is reason to believe that the initial cloud environment in the telecommunications industry should be dominated by each manufacturer's own "small" cloud, and have a certain degree of closure. Judging from the advantages that cloud computing brings to telecom operators, openness, high equipment utilization, scalability, and service deployment flexibility are the four most important characteristics. When the openness is temporarily not fully satisfied, how to make your own systems and products have cloud characteristics such as high equipment utilization, scalability, and service deployment flexibility is a must for current telecom equipment vendors.
Secondly, under the premise that cloud computing technology is not yet fully mature, different products have different driving forces towards cloud computing architecture due to different characteristics.
For business products, they are inherently equipped with the "one-point access, full network service" cloud feature, and business products are on the periphery of the telecommunications network. Cloudization will not cause the entire network to oscillate. Therefore, business products not only have the driving force of cloudization in business characteristics, but also the most suitable system equipment for clouding in network architecture.
For core network products, due to the core position of the network, and with the introduction of IMS, core network equipment has features such as detailed functions, many types of network elements, and flat network, which leads to the fault location when a network failure occurs Very high complexity. If the cloud platform is introduced when the cloud computing technology is not fully mature, it will increase the complexity of the core network and make it more difficult to locate the fault. Therefore, the cloudification of network equipment should be considered when the cloud computing technology is relatively mature.
For access equipment such as base stations, although the concept of "base station cloud" has emerged in the industry, due to the inherent "non-cloud" characteristics of geographical dispersion and small capacity, the driving force for cloud services is insufficient. The cloudization of access equipment should be the last equipment considered.
For network management equipment, the problem is more complicated than the main equipment. On the one hand, the NMS needs to solve the “cloud-oriented†problem of the NMS, that is, how the NMS provides management when other devices are running in the cloud environment; Problems running in the environment. The "cloud-oriented" problem of network management is a problem that needs to be solved first. As long as there is a device running in a cloud environment, it must provide management functions. As for the problem of cloud-based network management, if the network management center builds the network management of all equipment manufacturers on a cloud, then the current cloud platform is open and the standardization is not enough, which will cause greater risks. If the equipment manufacturers build their own network management "small cloud", the server used by the network management is too small compared to the business, and it is difficult to reflect the advantages of the cloud. Based on the above analysis, the issue of "cloud-based" can be considered one step later.
Without accumulating steps, there will be no thousands of miles; without accumulating small streams, there will be no rivers. Due to the openness of cloud computing, high equipment utilization, scalability, and service deployment flexibility, it is an inevitable trend to introduce cloud computing or devices with cloud computing features in the telecommunications field in the future. The road needs us to explore. For the telecommunications industry, it is our urgent task to analyze the different application requirements of different devices for cloud computing environments and prepare for the future of the cloud era.
This Automation curtain is specially designed for automation industry. SDKELI LSC2 light curtain is designed for automation field, with small size, compact structure and strong anti-interference ability, and the product meets IEC 61496-2 standards. The Automatic Light Curtain is with reliable quality and very competitive price. It has been used in many factories and has replaced curtains from Sick, Omron, Banner, Keyence, etc.
Automatic Light Curtain,Laser Light Curtain,Automation Light Beam Sensor,Automatic Infrared Beam Sensor,Infrared Beam Curttain Sensor,Infrared Beam Sensor
Jining KeLi Photoelectronic Industrial Co.,Ltd , https://www.sdkelien.com