Among the many combined system, INS/GPS integrated navigation system has developed rapidly and has been widely used in military and civilian fields, and it has received more and more attention. As far as the INS/GPS integrated navigation system is concerned, in addition to a large amount of navigation solution work, functions such as control, human-machine interface, and communication with external systems are also required. Since the navigation system has high requirements for real-time performance, it is unrealistic to use a single-chip CPU to implement the above functions. In the development of a missile-loaded INS/GPS integrated navigation system, an embedded high-speed processing system was designed for the small size, light weight and low power consumption of the missile-borne navigation system. The system uses TI's TMS320VC33 and TMS320F240 to form a dual DSP system, that is, two DSPs form a master-slave system to complete the corresponding functions. The key to master-slave system design is data communication between the master and slave. The main data communication between the master and the slave is serial, parallel, DMA and dual port RAM. Combining the advantages and disadvantages of various communication methods, considering the high real-time performance of the navigation system and the large amount of data, the author uses the dual-port RAM device CY7C028 as the shared memory. The author uses the dual-port RAM device CY7C028 as the shared memory through a unique software partition. The processing design effectively implements communication between the host computer and the slave microcomputer in the navigation system.
1 internal structure and working principle of dual-port RAM chip CY7C028CY7C028 is a 64K & TImes; 16 low-power CMOS static dual-port RAM developed by CYPRESS. The maximum access time is 12/15/20ns, which can be used with most high-speed processors without inserting a wait state. The master-slave mode makes it easy to expand the data bus to 32 bits or more. Its internal functional block diagram is shown in Figure 1.
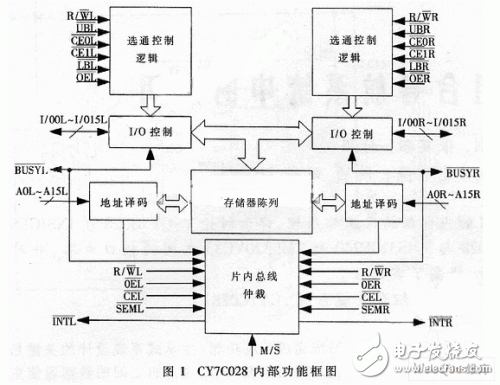
The dual-port RAM chip CY7C028 is a fast communication device with superior performance, and is very suitable for most CPU high-speed digital systems. Its features are: provide two sets of completely independent data lines, address lines, read and write control lines, allowing two CPUs to operate simultaneously on dual-port memories; with two sets of complete interrupt logic for implementing between two CPUs Handshake signal; has completely independent busy logic, which can protect two CPUs from correct reading and writing operations on the same address unit. When two CPUs access dual-port RAM, there are four cases.
(1) Two CPUs do not simultaneously access data to the same address unit.
(2) Two CPUs simultaneously read data from the same address unit.
(3) Two CPUs simultaneously write data to the same address unit.
(4) Two CPUs operate on the same address unit at the same time, one writes data and the other reads data.
It is not difficult to see that in the first and second cases, there is no error in accessing the two ports, and a write error occurs in the third case, and a read error occurs in the fourth case. In order to avoid data read and write errors caused by address data contention when two CPUs access the same address unit, CY7C028 mainly provides the following working methods, which are introduced one by one.
1.1 Hardware arbitration method
Dual Port RAM CY7C028 has hardware arbitration logic that addresses the simultaneous access of two processors to the same address location. In the two sets of control lines of the dual port RAM, there is one BUSY pin. When the CPUs at both ends do not access the same address unit of the dual port RAM, BUSYL=H, BUSYR=H, can be stored normally; when the CPUs at both ends access the same address unit of the dual port RAM, which port access request signal After it appears, its corresponding BUSY=L, prohibits its access to data; when it is impossible to determine the order in which the two port access request signals appear, only one of the control lines BUSYL and BUSYR is low. In this way, it can be ensured that the port corresponding to BUSY=H can perform normal access, and the port corresponding to BUSY=L cannot be accessed, thereby avoiding the possibility that two CPUs compete for address resources at the same time and cause an error.
1.2 Interrupt arbitration method
The interrupt arbitration method is also called the mailbox arbitration method. The CY7C028 has two sets of interrupt logic, which are respectively received on the interrupt pins of two CPUs through two INT pins to realize the CPU handshake. In the data transfer of the dual port RAM, the CPUs at both ends use the dual port RAM as part of their own memory. When two CPUs need data transfer, it is assumed that the left CPUL is transferred to the right CPUR. First, the CPUL stores the data to be transferred to a predetermined address unit of the dual port RAM, and then to the highest odd address unit of the dual port RAM, 0xFFFF, right. The port's mailbox is written to send an interrupt to the CPUR, so that the CPUR enters its corresponding interrupt service subroutine, reads the data of the agreed address unit, and then writes the mailbox of the right port of the dual port RAM. To clear the interrupt.
1.3 Token arbitration method
The token arbitration method is a fast data exchange method. In this mode, there is signaling latch logic. CY7C028 internally provides eight independent latch logic units, which can divide the RAM space into up to eight segments. These latch logic units are independent of the dual-port RAM memory area, and cannot control the RAM area and block the read/write operations of the CPUs at both ends. Instead, they are used as commands to provide only the instruction logic, which is rotated by the CPUs at both ends according to the agreed rules. The area occupies the RAM area defined by them. The size and address of each area are freely set by the software, and the left and right ends operate exactly the same, as long as the limit number of tokens is not exceeded. When the left and right ends apply for the same token at the same time, the token logically determines who is occupied first, thereby ensuring that only one port obtains the token. During the occupation of the token, the CPU can access the data at the highest speed without waiting, which is undoubtedly very advantageous for realizing high-speed, multi-CPU data acquisition and processing systems. However, in order to avoid the token mode contention error, the CPUs at both ends should occupy the same RAM area in time.
2 Dual port RAM application in integrated navigation system2.1 Overall system design
Conecting Terminals Without Screws
Conecting Terminals Without Screws,Cold Pressing Terminals,Low Pressure Cold Shrinkage Terminal,Cold Shrinkage Cable Terminals
Taixing Longyi Terminals Co.,Ltd. , https://www.lycopperterminals.com