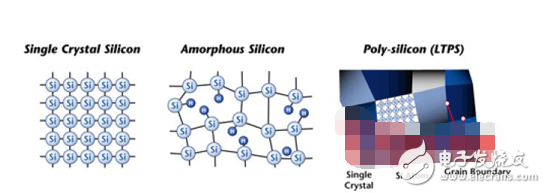
Low Temperature Poly-silicon (LTPS, hereinafter referred to as LTPS) is another new technology in the field of flat panel displays. Next-generation technology following amorphous silicon (Amorphous-Silicon, hereinafter referred to as a-Si).
Polysilicon is a silicon-based material of about 0.1 to several um, made up of many silicon particles. In the semiconductor manufacturing industry, polysilicon is usually processed by LPCVD (Low Pressure Chemical Vapor DeposiTIon) and then an annealing process higher than 900C, which is SPC (Solid Phase CrystallizaTIon). However, this method is not suitable for the flat panel display manufacturing industry because the maximum temperature of the glass is only 650 °C. Therefore, LTPS technology is specially applied to the manufacture of flat panel displays.
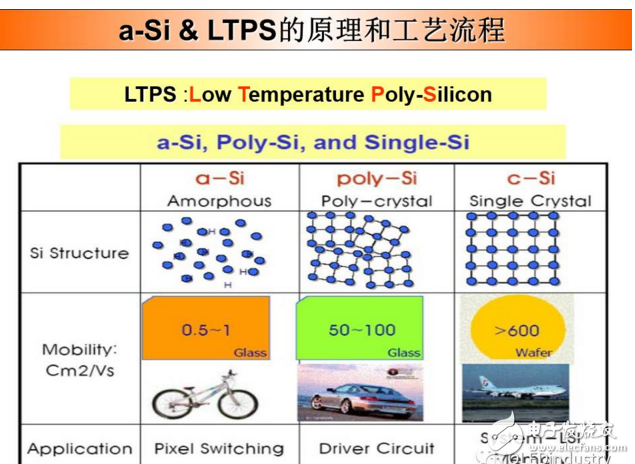
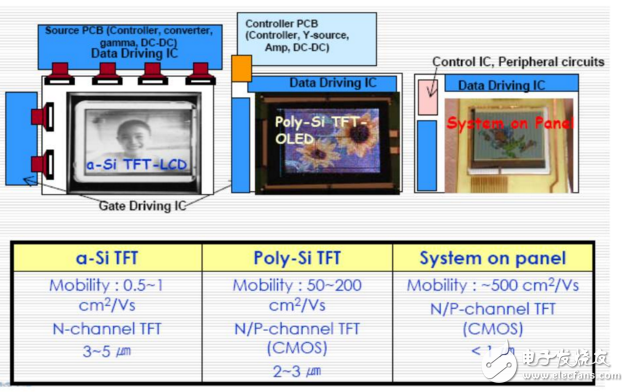
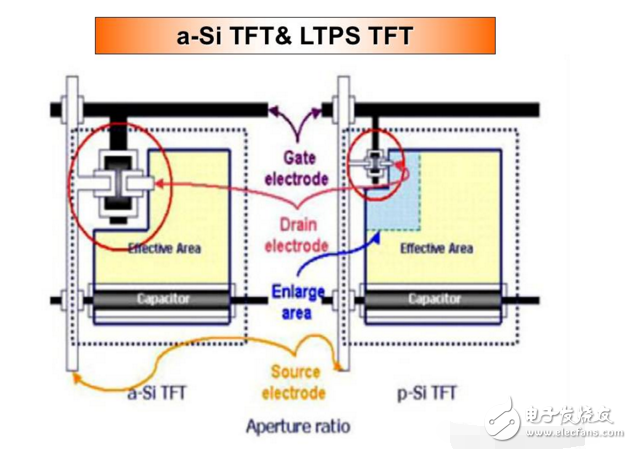
The traditional amorphous silicon material (a-Si) has an electron mobility of only 0.5 cm2/VS, while the low-temperature polysilicon material (LTPS) has an electron mobility of 50-200 cm2/VS, so it is electrically compared with a conventional amorphous silicon film. Compared with crystal liquid crystal display (a-Si TFT-LCD), low-temperature polysilicon TFT-LCD has the advantages of higher resolution, faster reaction speed, higher brightness (high aperture ratio), and the peripheral driving circuit can be simultaneously fabricated in glass. On the substrate, the goal of integrating on a glass system (SOG) is achieved, so space and cost can be saved. In addition, LTPS technology is a technology platform for developing active organic electroluminescence (AM-OLED), so the development of LTPS technology has been Wide attention.
Low Temperature Poly-silicon (LTPS) was originally developed by Japanese and American technology companies in order to reduce the energy consumption of Note-PC displays, making Note-PC appear thinner and lighter, and developed in the mid-nineties. The technology began to move toward the trial phase. The new generation of organic light-emitting liquid crystal panel OLEDs derived from LTPS was officially put into practical use in 1998. Its biggest advantage is its ultra-thin, light weight and low power consumption, which can provide more vivid colors and clearer images.
In the packaging process, the LCD display uses excimer laser as a heat source. After the laser light passes through the projection system, a laser beam with uniform energy distribution is generated, which is projected onto the glass substrate of the amorphous silicon structure, and is absorbed by the amorphous silicon structure glass substrate. After the energy of the excimer laser is converted into a polysilicon structure, since the entire process is completed below 600 ° C, the general glass substrate can be applied.
As an advanced representative of display technology, LTPS is currently gaining higher penetration rate in smart phones, and VR hardware (AMOLED is the standard display) is on the eve of the outbreak. From the demand side, the application of small and medium-sized LTPS panels in smartphones and tablets has been rising, and the AMOLED market has erupted ahead of the flexible display. Obviously, LTPS is already the core technology of AMOLED development. How much understanding is the principle structure of LTPS? This article extracts the data of LTPS before Tianma Zhao Bengang's teacher. Xiaobian will analyze LTPS in three parts. This weekend, Give everyone a little bit to compare and analyze amorphous silicon and LTPS.
Rotor Core,Copper Rotors,Copper Rotors With Shafts,Rotor Assembly
Henan Yongrong Power Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.hnyongrongglobal.com