AAC is an abbreviation for Advanced Audio Coding, which appeared in 1997 and was originally based on MPEG-2 audio coding technology. Co-developed by Fraunhofer IIS, Dolby Laboratories, AT & T, Sony and other companies, the purpose is to replace the MP3 format. In 2000, the MPEG-4 standard was introduced, and AAC reintegrated other technologies (PS, SBR). In order to distinguish it from the traditional MPEG-2 AAC, AAC with SBR or PS characteristics is also called MPEG-4 AAC.
AAC is a new generation of audio lossy compression technology. It derives the three main encodings of LC-AAC, HE-AAC, and HE-AACv2 through some additional encoding technologies (such as PS, SBR, etc.). LC-AAC is Compared with traditional AAC, relatively speaking, it is mainly used for medium and high code rate (》 = 80Kbps), HE-AAC (equivalent to AAC + SBR) is mainly used for low and medium code (》 = 80Kbps), and the newly launched HE-AACv2 (Equivalent to AAC + SBR + PS) Mainly used for low bit rate ("= 48Kbps), in fact, most encoders are set to" = 48Kbps automatically enable PS technology, and "48Kbps without PS, it is equivalent to ordinary HE-AAC.
2. Brief description of AAC specificationsAAC has 9 specifications to meet the needs of different occasions:
MPEG-2 AAC LC Low Complexity (Low Complexity)-relatively simple, no gain control, but improved
Coding efficiency, you can find a balance in the coding efficiency of medium bit rate and sound quality
MPEG-2 AAC Main specifications
MPEG-2 AAC SSR Variable Sample Rate Specification (Scaleable Sample Rate)
MPEG-4 AAC LC Low Complexity (Low Complexity) --- Nowadays mobile phones are more common in MP4 files
The audio part of the includes the audio file of this specification
MPEG-4 AAC Main main specification ------ includes all functions except gain control, its sound quality is the best
MPEG-4 AAC SSR Variable Sample Rate Specification (Scaleable Sample Rate)
MPEG-4 AAC LTP Long Term PrediciTIon
MPEG-4 AAC LD Low Delay Specification (Low Delay)
MPEG-4 AAC HE High Efficiency Specification ----- This specification is suitable for low bit rate coding, there are
Nero ACC encoder support
Currently the most used are LC and HE (suitable for low bit rate). The popular Nero AAC encoding program only supports the three specifications of LC, HE, and HEv2. After encoding, the AAC audio and specifications are displayed in LC. HE is actually AAC (LC) + SBR technology, HEv2 is AAC (LC) + SBR + PS technology;
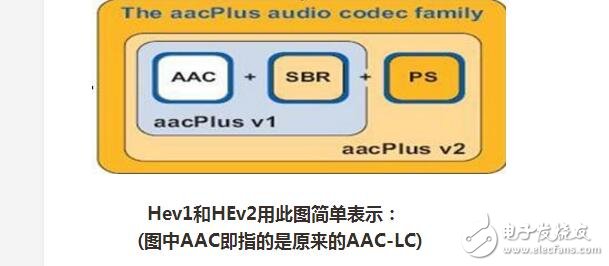
HE: "High Efficiency". HE-AAC v1 (also known as AACPlusV1, SBR), using container method to achieve AAC (LC) + SBR technology. SBR actually stands for Spectral Band ReplicaTIon (band replication). Briefly, the main spectrum of music is concentrated in the low frequency band, and the amplitude of the high frequency band is very small, but it is very important and determines the sound quality. If the entire frequency band is coded, if it is to protect the high frequency, the low frequency band coding will be too fine and the file will be huge; if the main component of the low frequency is saved and the high frequency component is lost, the sound quality will be lost. SBR cuts the spectrum, separates the main components of the low-frequency encoding and preserves the sound quality by separately amplifying and encoding the high-frequency, "integrated", and saves the sound quality while reducing the file size, which perfectly resolves this contradiction.
HEv2: The method of using containers includes HE-AAC v1 and PS technology. PS refers to "parametric stereo" (parametric stereo). The original stereo file is twice the file size of one channel. However, there is some similarity between the sounds of the two channels. According to Shannon's information entropy coding theorem, the correlation should be removed to reduce the file size. Therefore, PS technology stores all the information of one channel, and then spends a few bytes to describe the difference between another channel and it with parameters.
3. Features of AAC(1) AAC is an audio compression algorithm with a high compression ratio, but its compression ratio far exceeds that of older audio compression algorithms.
Such as AC-3, MP3, etc. And its quality is comparable to the uncompressed CD sound quality.
(2) Like other similar audio coding algorithms, AAC also uses transform coding algorithm, but AAC uses resolution
Higher filter bank, so it can achieve higher compression ratio.
(3) AAC uses the latest technologies such as temporary noise reshaping, backward adaptive linear prediction, joint stereo technology and quantized Huffman coding. The use of these new technologies has further improved the compression ratio.
(4) AAC supports more sampling rates and bit rates, supports 1 to 48 audio tracks, supports up to 15 low-frequency audio tracks, has
Multi-language compatibility and up to 15 embedded data streams.
(5) AAC supports a wider range of sound frequencies, up to 96kHz, up to 8KHz, which is much wider than the 16KHz-48kHz range of MP3.
(6) Unlike MP3 and WMA, AAC hardly loses the very high and very low frequency components in the sound frequency, and is closer to the original audio frequency spectrum structure than WMA, so the sound fidelity is better. Professional evaluation shows that AAC sounds clearer than WMA and is closer to the original sound.
(7) AAC uses optimized algorithms to achieve higher decoding efficiency, requiring less processing power when decoding.
4. AAC audio file format1. The audio file format of AAC is ADIF & ADTS:
ADIF: Audio Data Interchange Format. The characteristic of this format is that the start of the audio data can be determined without decoding in the middle of the audio data stream, that is, its decoding must be performed at a clearly defined start. Therefore, this format is commonly used in disk files.
ADTS: Audio Data Transport Stream. The characteristic of this format is that it is a bit stream with sync words, and decoding can start anywhere in this stream. Its characteristics are similar to the mp3 data stream format.
Simply put, ADTS can be decoded in any frame, which means that it has header information every frame. ADIF has only one unified header, so all data must be decoded. The formats of these two headers are also different. At present, generally encoded and extracted audio streams in the ADTS format. The specific organizational structure of the two is as follows:
AAC's ADIF format is shown below:

The general format of AAC's ADTS is shown below:

The figure shows the simple structure of one frame of ADTS, and the blank rectangles on both sides represent the data before and after one frame.
2. ADIF and ADTS header
ADIF header information:
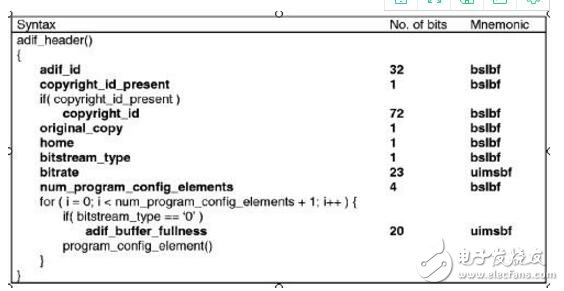
The ADIF header information is located at the beginning of the AAC file, followed by continuous raw data blocks.
The fields that make up the ADIF header information are as follows:

ADTS fixed header information:

ADTS variable header information:

(1) The purpose of frame synchronization is to find out the position of the frame header in the bit stream. According to 13818-7, the frame header in aac ADTS format
The sync word is 12-bit "1111 1111 1111".
(2) ADTS header information consists of two parts, one is fixed header information, followed by variable header information. Fixed header information
The data is the same every frame, and the variable header information is variable from frame to frame.
3. AAC element information
In AAC, the composition of the original data block may have six different elements:
SCE: Single Channel Element. The single channel element basically consists of only one ICS. One
The original data block is most likely composed of 16 SCEs.
CPE: Channel Pair Element Dual channel element, consisting of two ICS and some joint stereos that may share side information
Composed of vocoding information. A raw data block may consist of up to 16 SCEs.
CCE: Coupling Channel Element. Multi-channel joint stereo information representing a block
Or dialogue information for multilingual programs.
LFE: Low Frequency Element. Contains a channel to enhance the low sampling frequency.
DSE: Data Stream Element data stream element, contains some additional information that is not audio.
PCE: Program Config Element program configuration element. Contains channel configuration information. It may appear in
ADIF header information.
FIL: Fill Element. Contains some extended information. Such as SBR, dynamic range control information, etc.
4. AAC file processing flow
(1) Judge the file format and determine it as ADIF or ADTS
(2) If it is ADIF, solve the ADIF header information and skip to step 6.
(3) If it is ADTS, look for the sync header.
(4) Decode the ADTS frame header information.
(5) If there is error detection, perform error detection.
(6) Deblocking information.
(7) Solution element information.
Product Name: Car Charger
Place of Origin: Guangdong, China (Mainland)
Brand Name: OEM
Output Type: DC
Connection: Other
Rated Voltage: 12V-24V
Working Temp: 0-55℃
Weight: 36g
Materials: PC+ABS
Color: White Black
Warranty: 1 year
Suitable for:Most digital devices
SMART PROTECTION & ATTRACTIVE DESIGN ------ Intelligent circuit design protects against short circuiting,over-heating,over-current,and over-charging. Charging stops when battery is full. Car charger with blue LED indicator,which makes it convenient to find exactly where the connection should go; And the light is soft enough not to distract at night.
Dual USB Car Charger Adapter,USB Smart Port Charger ,Car Charger,USB Car Charger For Phone
Shenzhen Waweis Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.waweispowerasdapter.com