Abstract With the implementation of the national energy policy, power plants use more and more high-voltage inverters to drive motors. The paper introduces the new inverter motor differential protection device developed by a certain technology company. It uses the sampling value differential principle to realize the differential protection of the inverter motor. The transformer and motor protection functions are integrated into one device and passed. The hard pressure plate that is switched by the bypass switch performs the function of backup protection.
Keywords motor protection; transformer protection; phasor differential; sampled value differential; bypass switch
According to the requirements of the national energy policy, energy conservation and emission reduction work has been fully carried out, and in large thermal power plants, the reduction of power consumption rate of the plant is imperative. For high-voltage motors that account for most of the plant's electricity consumption, an important technical measure in the field of energy conservation is the application of high-voltage frequency conversion technology. With the development of power electronics technology, frequency converters have been widely used in power plants. At present, new auxiliary power plants, important auxiliary machines such as fans and pumps, are generally required to consider the configuration of frequency converter dragging; more and more established power plants are undergoing or have completed the transformation of high-voltage motors using frequency converters. After the high-voltage motor is driven by the inverter, how to configure the motor protection can ensure the safe and reliable operation of the unit, which becomes a concern of power plants, design institutes and protection manufacturers.
The faults of the asynchronous motor include the stator winding phase-to-phase short-circuit fault, the winding inter-turn short-circuit fault and the single-phase ground fault; the abnormal operating state mainly has overload, stall, long starting time, three-phase power imbalance or phase-fault operation, Abnormal voltage, etc. Therefore, for high-voltage motors, differential protection or current quick-break protection is the main protection according to the regulations, and overload protection, over-current protection, negative-sequence protection, zero-sequence protection and low-voltage protection are used as backup protection.
In order to ensure the reliability of the power plant, the high-voltage motor generally adopts the frequency converter with power frequency bypass, so that even when the inverter is inspected, it can be bypassed by the power frequency to ensure the normal operation of the motor. Figure 1 is a schematic diagram of the transformation of the high-voltage motor inverter in the field. The K1 and K2 switches ensure that there is no contact point with the main circuit when the inverter is inspected. At this time, the K3 switch is closed and the motor runs through the bypass.
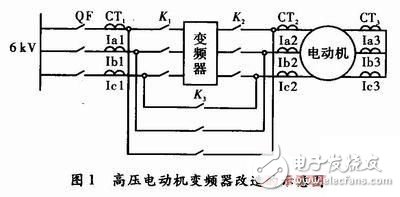
When the motor runs through the bypass, the motor directly drives the motor from the power frequency of the high-voltage busbar in the factory. The protection device of the protection device at the incoming switch QF is the switch outlet and the motor body. Therefore, at this time, the motor protection should be configured according to the requirements of conventional motor protection. If differential protection is required, motor differential protection needs to be configured.
When the bypass switch K3 is disconnected and the motor is dragged by the inverter, the protection object of the protection device at the incoming line switch QF is the switch outlet and the inverter. Since the inverter used in the current power plant is generally composed of a rectifier transformer, a control cabinet, and the like, that is, the protection device of the inlet switch QF is a switch outlet and a rectifier transformer. At this time, the motor becomes the load of the high-voltage inverter after being isolated from the factory bus, so the protection of the motor should be realized by the controller of the high-voltage inverter system. For 6 to 10 kV rectifier transformers, conventional transformer backup protection is generally configured, and there is a slight difference between the timing and the conventional transformer. At this time, the conventional differential protection of the motor cannot be differentially protected due to the inconsistency between the current at the switch and the current frequency at the neutral side of the motor, and can only be withdrawn.
At present, the general inverter motor protection configuration includes: motor protection measurement and control device, motor differential protection device, and transformer protection measurement and control device. The motor protection device and the transformer protection device perform the function retraction through the bypass switch: that is, the bypass switch is disconnected, at this time, the inverter drives the motor mode, the transformer protection device is put in, the motor protection device and the motor differential protection device are withdrawn; When the bypass switch is closed, the motor is directly dragged by the power frequency grid, the motor protection device and the motor differential protection device are put into operation, and the transformer protection device is withdrawn.
Iget series
Nanning Ousibang Information Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.ousibangvape.com