DSP Digital Signal Processing (DSP) is an emerging discipline that covers many disciplines and is widely used in many fields. Since the 1960s, with the rapid development of computer and information technology, digital signal processing technology has emerged and developed rapidly. Digital signal processing is a method of processing real-world signals by performing transformations or extracting information using mathematical techniques, and these signals are represented by a sequence of numbers. In the past two decades, digital signal processing has been widely used in communications and other fields.
DSP principle and characteristics
Digital signal processing is the theory and technique of digitally representing and processing signals. Digital signal processing and analog signal processing are a subset of signal processing. The DPS principle is to use a computer or a dedicated processing device to collect, transform, filter, estimate, enhance, compress, and recognize signals in digital form to obtain a signal form that meets people's needs.
The purpose of digital signal processing is to measure or filter real-world continuous analog signals. Therefore, it is necessary to convert the signal from the analog domain to the digital domain before performing digital signal processing, which is usually implemented by an analog to digital converter. The output of digital signal processing is often also transformed into the analog domain, which is achieved by a digital-to-analog converter.
Digital signal processing algorithms require the use of computers or specialized processing devices such as digital signal processors (DSPs) and application specific integrated circuits (ASICs). Digital signal processing technology and equipment have the advantages of flexibility, accuracy, strong anti-interference, small size, low cost, and high speed. These are unmatched by analog signal processing technology and equipment.
Digital signal processing is implemented in many ways, such as software (such as Fortran, C language) on a general-purpose computer; dedicated acceleration processor implementation in a general-purpose computer system; implemented by a general-purpose microcontroller, this method can be used for some Less complex digital signal processing, such as digital control;
Implemented with a general-purpose programmable DSP chip. Compared with single-chip microcomputers, DSP chips have more software and hardware resources suitable for digital signal processing, and can be used for complex digital signal processing algorithms;
It is realized by a dedicated DSP chip. In some special occasions, the required signal processing speed is extremely high, which is difficult to implement with a general-purpose DSP chip, such as a DSP chip dedicated to FFT, digital filtering, convolution, etc., which will correspond accordingly. The signal processing algorithm is implemented in hardware inside the chip without software programming.
DSP generally adopts the Harvard structure separated from the data bus and the program bus, allowing the instruction fetch and the execution instruction to be completely overlapped; the information can be directly transmitted between the program and the data space, and the access conflict is reduced, thereby obtaining high-speed computing capability.
Moreover, most of the pipeline technology is used, that is, each instruction is completed by multiple functional units on the chip, such as fetching, decoding, fetching, and executing, thereby reducing the execution time of each instruction without increasing the clock frequency. . DSPs usually have more than three stages of pipeline.
Multiple operations are performed every clock cycle. For filtering, correlation, matrix operations, etc., which require a large number of multiply-accumulate operations, DSPs are mostly equipped with independent multipliers and adders, so that multiplication and accumulation can be performed in the same cycle. Some DSPs can perform multiplication, addition, and subtraction operations at the same time, which greatly speeds up the butterfly operation speed of the FFT.
DSP system application field
(1) General digital signal processing: digital filtering, convolution, correlation, FFT, adaptive filtering, waveform generation, and the like.
(2) Communication field: high-speed modem, code/decoder, fax, program-controlled switch, satellite communication, IP telephone, etc.
(3) Speech processing: speech recognition, synthesis, vector coding, voice mail, etc.
Typical DSP system
The smallest system consisting of DSP devices as the core includes voltage regulators, reset circuits, crystal oscillators, as well as program memory and data memory (usually using internal resources of DSP devices)
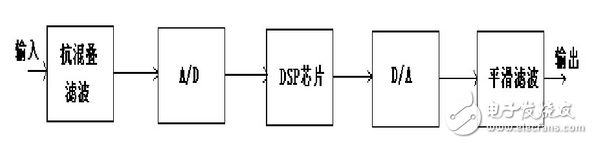
Typical DSP system
Class 2 Power Adapter,Class 2 Power Adaptor 24V,1.5Amp Class 2 Adaptor,1.5A Switching Adaptor
ShenZhen Yinghuiyuan Electronics Co.,Ltd , https://www.yhypoweradapter.com