The emergence of the Internet has magnified the social attributes of people. With the expansion of cyberspace, the network will become an integral part of people's work and life. In the future, anyone can access the services and information they need on the Internet, anytime, anywhere, on the Internet. At this point, the network infrastructure presents more "transparent" characteristics to the user (ie, the user does not need to feel the presence of the network when obtaining services and information). This puts higher requirements on the underlying network infrastructure, far beyond traditional network standards in terms of coverage, access bandwidth, network security, and reliability and scalability.
As the infrastructure of the information age, broadband is an important foundation for the country's economic and social development and one of the important criteria for measuring national competitiveness. In 2010, members of the United Nations Broadband Commission signed the Declaration on the Future of Broadband, which is considered the basic legal right of citizens. At present, nearly 100 countries and regions have launched national broadband plans.
The Internet and the informationization process have accompanied each other. The process of industrialization and information integration has injected new vitality into the development of the Internet. The connection between people, people, things, and things is the main form of the Internet in the future. Therefore, converged bearers, scale expansion, green environmental protection, security and trustworthiness, and ultra-broadband access (above 100 Mbit/s) will become the basic requirements for network infrastructure in the future Internet context.
This paper starts with the demand of the Internet for the network infrastructure in the future, and takes the UWB network related technology as the research object. On the basis of analyzing and studying the basic requirements of the UWB network, it focuses on the key technologies in the UWB network architecture.
2 Basic requirements for ultra-broadband networksThe development of technology must be people-oriented and the network as well. The development of ultra-broadband networks must be centered on meeting the needs of users' informationization.
(1) Ultra-large-scale ultra-wideband access
With the scale development and application of technologies such as the Internet of Things, cloud computing and rich media, the scale of users and terminals has further expanded. If the metropolitan area network is used as the unit, the user scale exceeds 10 million, and the terminal scale exceeds 100 million yuan, which will become an important feature of the future broadband network. The rapid development of technologies such as video services and virtual reality has greatly boosted the demand for bandwidth for users. For a long period of time in the future, bandwidth will remain the primary demand of users. The per capita bandwidth of 100 Mbit/s will be the basic requirement for broadband access in the future.
(2) extensive coverage
With the advancement of the integration of informatization and industrialization, secure access anytime, anywhere, any terminal and any way has become the basic needs of users for information services. The convergence of network coverage and physical space has become the trend of the times, and ubiquitous access has become one of the basic requirements of ultra-wideband networks.
(3) Converged bearer
With the enrichment and development of network applications, the traditional chimney-based network construction model that closely matches the network-business is unsustainable, and the network convergence bearer trend based on IP technology is irreversible. Under the ALL-IP architecture, all applications and services, including video, audio, data, and mobile, should be converged over the same network.
(4) Ultra high reliability
Bearer reliability is the basic condition for multi-service convergence bearers. Ultra-broadband networks should be able to achieve ultra-high reliability indicators for critical services (99.9999%). At full load, the critical node and critical link failure switching time should be less than 50ms.
(5) Green energy saving
Green energy conservation is a necessary condition for the sustainable development of broadband networks. In the operation of ultra-wideband networks, it is necessary to reduce the energy consumption per bit and improve the efficiency of each bit of bearer, improve network performance, and effectively reduce unit energy consumption.
(6) Security and credibility
The openness and ubiquity of the Internet is pushing the network and information security to unprecedented heights. A secure and trusted network is critical to the continued healthy development of the Internet. While building an ultra-broadband network infrastructure, it is necessary to establish a comprehensive user/network/service security system to create an end-to-end integrated security assurance capability to ensure the security of users, networks and services in an ultra-wideband network environment.
(7) Smooth evolution
The smooth evolution of the network is an important guarantee for the sustainable development of the network. In the process of building an ultra-wideband network, the smooth evolution of the network should be ensured from the aspects of network equipment reusability, network architecture scalability, and network capability upgradeability.
(8) Intelligent control
User experience and network performance are two key propositions in the development of the Internet. Providing users with an "on-Demand" user experience is a typical feature of the future Internet. The “on-demand†user experience requires network resources to be intelligently managed and provisioned, and this intelligent management capability relies on user-network-business coordination.
(9) IPv6 technology and service enablement
In the future, access to mass terminals and "always-on" service features require ultra-broadband networks with sufficient addressing space. The IPv4 address space is difficult to meet the development of ultra-wideband networks. Therefore, the ultra-broadband network must be an IPv6 technology and a service-enabled network.
3 Research on key technologies of ultra-wideband networksThe ultra-broadband network system achieves strong support for the future Internet by organically integrating the three types of capabilities of network transmission, computing and storage. A complete UWB network architecture requires key technologies such as efficient bearer, reliable protection, security and credibility, intelligent management, green energy conservation and experience enhancement. Security and credibility and intelligent management technology involve coordination and resource scheduling at multiple levels such as users, networks and services. This paper mainly analyzes and studies related technologies from the perspective of network bearer, and does not elaborate on technologies such as security credibility and experience enhancement.
3.1 Efficient bearer technologyUnder the ALL-IP architecture, key technologies supporting efficient bearer include IPoE, IP and transport coordination, and network-platform collaboration.
(1) IPoE is based on the DHCP protocol extension, which can implement wide-area IP packet authentication, authorization, accounting, and effective transmission. Compared with the currently widely used PPPoE, the advantage of IPoE is not only the simplification of the encapsulation structure, but also the improvement of the multicast distribution efficiency. In the PPPoE access mode, the PPP connection and multicast between the user and the access control gateway are The replication of packets can be performed on a per-user basis. The actual effect is similar to that of a unicast bearer. In IPoE mode, multicast packets are replicated based on ports or VLANs. If you use cross-VLAN multicast, you can implement more efficient multicast distribution. . Under the condition of large-scale live broadcast service, the IPoE mode can move the multicast replication point from the access control gateway to the access network and other locations, further improving the multicast distribution efficiency.
(2) IP and transmission cooperation mainly refers to the cooperation between the IP and the OTN. In this mode, the channel-based OTN technology is introduced on the router or the VLAN sub-interface technology is introduced on the OTN to implement the interworking between the router and the OTN device on the physical interface. The GMPLS protocol is used to uniformly schedule network traffic to implement traffic optimization bearer under effective cooperation between the IP layer and the optical layer. In order to meet the UWB network architecture and service bearer requirements, the resource scheduling and flexible networking capabilities of the OTN must be improved. Specifically, the port aggregation and traffic aggregation capabilities of the OTN device can be enhanced to achieve more flexible resource scheduling. Currently, EOO ( Technologies such as Ethernet Over OTN) are typical representatives.
(3) Network-platform collaboration Currently mainly refers to CDN-based video content push. According to IBM research, storage costs have fallen at an average rate of 3% per week over the past 25 years, much faster than the cost of network bandwidth. On the other hand, the way to get video content nearby can significantly improve the user experience. Network-platform collaboration is based on the concept of “storage-for-bandwidthâ€, which introduces the CDN platform into the network to further improve the user experience while alleviating bandwidth pressure. CDN's intelligent segmentation and content intelligence "pull" technology can further improve content push efficiency, which is the focus of research in this field. In addition, the integration of CDN functions into network devices to achieve network-business is more organic and synergistic, becoming the main trend in this field.
3.2 Business Reliability Guarantee TechnologyBearer reliability is the fundamental guarantee for service reliability. Due to the “best effort†feature of IP networks, the reliability under IP integrated bearer conditions is always a key concern in the IP network construction process. IP network reliability is primarily achieved through fast fault detection and topology/device redundancy.
The role of different NEs/links in the network is different, and the role in reliability assurance is not the same. Starting from key network elements/links, targeting and improving network reliability are the focus of UWB networks. In the UWB network, the access control device not only bears the traffic forwarding and control functions, but also bears some functions of user management, and is the most important network element in the service reliability guarantee link. Therefore, the reliability of access control equipment is an important guarantee for the reliability of ultra-wideband network services. The reliability of access control devices is mainly achieved through seamless hot standby technology across the chassis. The principle of seamless hot standby technology across the chassis is shown in Figure 1. Based on the synchronization of user information and VRRP and BFD technologies, the critical node and critical link fault switching time can be less than 50ms under full load. Based on this, combined with fast route convergence and other technologies, it can achieve ultra-high reliability indicators (99.9999%) for key services such as video and audiovisual.
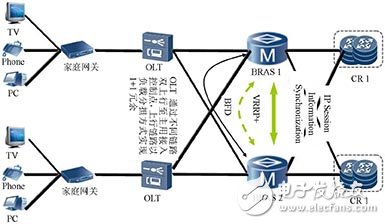
Figure 1 Principle of seamless hot standby technology across chassis
The development of network virtualization technology has made it possible to implement reliability assurance in a wider range. Currently, related technologies such as pooling and clustering of access control devices can achieve reliability guarantee in a wider range.
3.3 Green energy-saving technologyGreen energy conservation is reflected in equipment R&D, network design and operation. High integration, low energy consumption and large capacity are the basic requirements for equipment development. In addition to the equipment architecture design, the impact of chip technology level on equipment energy consumption is very obvious. In general, an increase in the level of technology will result in a substantial reduction in energy consumption. At present, the chip technology of network equipment is mainly concentrated at the 65nm level, and will transition to the 45nm and 32nm process levels in the future. The ultra-broadband network is mainly built on the optical network technology, which improves the network capacity while improving the network performance. In the access part, the PON technology is mainly used to implement full-service full-service access, while in the backbone part, IP-transmission coordination is adopted. Realize optical network bearer. In the network operation process, the user-network-business integrated intelligent coordination system is mainly used to improve the overall operation level of the network and reduce the energy consumption.
3.4 Experience Enhancement TechnologyThe eternal pursuit of user experience is the driving force behind the development of information society. The video service has the highest user experience requirements in all Internet services. Therefore, the user experience improvement is mainly focused on the improvement of the video service experience. Due to the long connection, high bandwidth, and sensitive user experience of video services, the development of large-scale video services poses great challenges to network capacity and carrying capacity. The video experience enhancement is mainly based on video enhancement technology.
Video enhancement technology enables video content retransmission and caching through video service processing and storage. Based on video enhancement technology, video switching time can be greatly shortened and picture quality can be greatly improved. Video enhancement technology improves the video user experience, and through IP and storage technology collaboration, shortens the traffic path, optimizes the network traffic model, and improves bandwidth efficiency. In the future, video service functions will gradually be integrated on network element devices.
Based on the deployment of video enhancement technology, real-time monitoring of video services can be formed by means of flow detection, such as rapid demarcation and positioning of video faults.
4 ConclusionThe foundation for determining the future of Internet development is the network infrastructure. Ultra-broadband networks are the inheritance and innovation of traditional broadband networks. Compared with the traditional broadband network, the ultra-broadband network organically integrates the transmission, computing and storage capabilities of the network, which can better meet the future development needs of the Internet. The operation and development of ultra-broadband networks depend on the development of broadband industry and technological innovation. Only by effectively integrating the power of the industry chain, ultra-broadband networks can enter a faster and healthier development track to better support the future development of the Internet.
We produce Lighting for commerical ,industrial ,and household . Specially for desk lamp LED which 360 degree bent freely .It can brighten you in any angle as
you want. Road light and functional light also.
Home Outdoor Lighting LED Stadium Light LED Floodlight LED Tri-proof Light LED Street Light LED Garden Light LED Canopy Light Indoor Lighting LED Panel Light LED Batten Light GL Series LED Batten Light GLK Series LED Batten Light
Home Lighting & Furnishings - Quality, Style and Selection. Lamps Plus offers a complete selection of indoor and outdoor lighting fixtures. From stylish ceiling light fixtures, chandeliers and trend-setting ceiling fans to thousands of designer lamps and lamp shades that are in-stock and ready to ship.
Home Light,Led Desk Lamp,Rgb Night Lamp,Bathroom Lights
Jiangmen soundrace electronics and technology co.,ltd. , https://www.soundracegroup.com