(Researchers of the Key Laboratory of Fluid and Power Machinery Ministry of Education (Xihua University) Liu Lingwei, Lei Xia, Li Zhu, Huang Guihong, Lei Hai, in the 22nd issue of Journal of Electrical Engineering, 2017, pointed out that electric vehicles change stations Due to its short-time and easy-to-manage management, it has become an important way to supplement electric vehicles. However, due to the randomness of electric vehicle users' power exchange requirements, current prediction methods cannot predict them accurately. Therefore, it is difficult to accurately define the charging and discharging scheduling plan for the power station.
Aiming at this problem, a pre-distribution and real-time scheduling model of the power station was established, and the simulation calculation was completed in Matlab by particle swarm optimization. In the day-to-day scheduling model, the pre-planning plan is formulated by predicting the user's power-replacement requirements, and the charging and discharging power of each sub-station is optimized under the premise of meeting the demand of each time period; in the real-time scheduling model, the error is predicted according to the demand forecast of each time period. Adjust the scheduling plan for subsequent time periods. Through the coordination of real-time scheduling and daily dispatching, the power station can suppress the impact of users' actual demand fluctuations, and at the same time reasonably take into account the interests of users, the benefits of power plant replacement and the optimal operation of the power grid.
With the global warming trend intensifying and the depletion of petroleum resources, the development of new energy electric vehicles is the trend of the times [1, 2]. Compared with traditional cars that use fossil energy as fuel, electric vehicles have incomparable advantages in energy conservation, emission reduction and environmental protection. With the popularization of electric vehicles in the future, electric vehicles will be connected to the power grid on a large scale, and disorderly charging and discharging will have a negligible impact on the safe and stable operation of the power grid [3-5]. Therefore, for the large-scale charging and discharging of electric vehicles, it is necessary to adopt a reliable scheduling strategy to centrally dispatch electric vehicles.
The literature [6] determines the scheduling priority of the vehicle based on the user's declaration information and the evaluation index system, and the agent formulates the scheduling plan of the vehicle according to the scheduling priority. Literature [7] proposes the concept of user satisfaction, and describes the user satisfaction by weighted combination of charge and discharge cost and rationality of scheduling plan, and establishes an optimal scheduling model with the goal of maximizing user satisfaction.
Literature [8,9] applied the two-layer optimization model to the charge and discharge scheduling of electric vehicles. The literature [8] added the wind power generation model to the optimal scheduling model based on the literature [7] to realize operators, power grids and users. The organic coordination of interests between the three. In [9], the variance of the total system load level is minimized to the upper target, and the two-level optimization model is established for the lower target with the consistency of the upper-level scheduling plan. However, it is more difficult to implement the vehicle owner declaration system.
The above literatures all study the vehicle charging mode. However, the charging and discharging authority of the electric vehicle in the vehicle charging mode belongs to each user, so that the charging station cannot make unified scheduling decisions [10]. Compared with the vehicle charging mode, the power-switching mode realizes the decoupling between the power battery and the vehicle. The charging and discharging behavior of the battery is more controllable and flexible, and it can effectively suppress the adverse effects on the power grid, and is more in line with the user. The willingness to wait for zero [11,12].
In [13], based on the literature [9], the dynamic optimization mechanism is adopted, and the charge and discharge prediction of the non-incoming vehicle is taken into account. The real-time charge and discharge scheduling of the substation is realized, but the scheduling result is affected by the prediction accuracy. Literature [14] analyzed the battery scheduling strategy based on response time-of-use electricity price, which can save the charging cost of the power station while restraining the load fluctuation of the power grid. The literature [15] proposes that the replacement power station will provide the battery to the user that is not fully charged during the peak period of power exchange, and give the user a certain discount according to the battery power to reduce the loss of customers and improve the income of the power station.
In [16], the concept of battery redundancy is proposed for the problem of the number of battery packs in different time periods of electric vehicles after scale-up. The condition of the time of power-requirement is obtained by analyzing the habits of the vehicle owners, so as to obtain the battery reserves in different periods. Number of groups. On the basis of the literature [6], the literature [7] takes the total charging power as the optimization variable to suppress the grid load fluctuation as the optimization goal, analyzes the scheduling results under different battery redundancy in the power station, and analyzes the difference. The pros and cons of battery redundancy.
In summary, the current literature on electric vehicle scheduling is mostly a static scheduling mode, and the fluctuation of actual user demand has a greater impact on scheduling. Based on the power-changing mode, this paper establishes a daily scheduling and real-time scheduling model based on the system time-sharing price.
In the day-to-day scheduling model, the substation develops a pre-planning plan according to the user's demand forecast, and satisfies the user's demand, to stabilize the grid load fluctuation and increase the yield of the power station. In the real-time scheduling model, the substation is based on the next day. The actual user demand in each period is corrected for the demand forecast of the subsequent period. On the basis of the daily scheduling, the scheduling plan of the subsequent period is dynamically adjusted, and the deviation between the adjustment result of the real-time scheduling of the substation and the previous scheduling plan is the optimization target.
Through the day-to-day scheduling and real-time scheduling model, the power station can suppress the fluctuation of actual user demand, and at the same time reasonably take into account the interests of users, the benefits of power plant replacement and the optimal operation of the power grid.
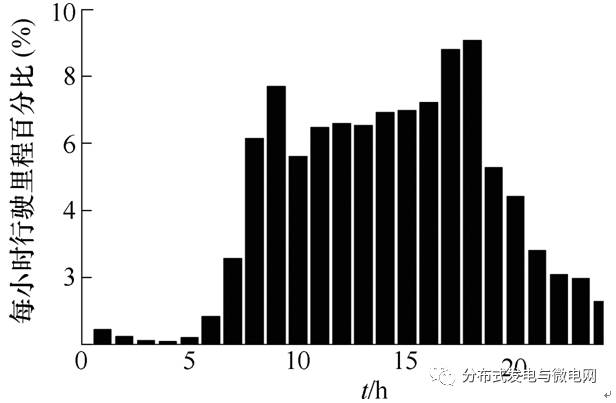
Figure 1 Percentage of driving distance of private cars in each period
in conclusion
In this paper, the subsequent demand forecast is corrected according to the actual needs of users in each period. Based on the daily dispatching, the scheduling plan is dynamically adjusted. On the basis of the power station can maximize the satisfaction of the user's demand, the power station's own revenue and grid load curve are used. Improved coordination establishes a charge and discharge scheduling model for the optimization goal and solves it by particle swarm optimization. The results show that the optimal scheduling can avoid the battery shortage, and fully utilize the energy storage characteristics of the battery to effectively suppress the load fluctuation of the power grid, play the role of cutting the peak and filling the valley, and maximize the return of the power station.
A power cord, line cord, or mains cable is an electrical cable that temporarily connects an appliance to the mains electricity supply via a wall socket or extension cord. The terms are generally used for cables using a power plug to connect to a single-phase alternating current power source at the local line voltage-(generally 100 to 240 volts, depending on the location). The terms power cable, mains lead, flex or kettle lead are also used. A lamp cord (also known as a zip cord) is a light-weight, ungrounded, single-insulated two-wire cord used for small loads such as a table or floor lamp.
Power Cord,Home Appliance Power Cord,Power Cable Cord
Dongguan YAC Electric Co,. LTD. , https://www.yacentercns.com